Goto, Hitoshi
| Affiliation | Information and Media Center |
|---|---|
| Concurrent post | Center for IT-Based Education (CITE) Research Center for Agrotechnology and Biotechnology Department of Computer Science and Engineering |
| Title | Professor |
| Fields of Research | Computational Chemistry / Chem-Bio Infomatics / High-Performance Computing |
| Degree | Ph. D. (Hokkaido University) |
| Academic Societies | Chemical Society of Japan / Americal Chemical Society / Society of Computer Chemistry, Japan / Chem-Bio Infomatics Society |
| gotoh@ Please append "tut.jp" to the end of the address above. |
|
| Laboratory website URL | http://www.cch.cs.tut.ac.jp/ |
| Researcher information URL(researchmap) | Researcher information |
Research
It is very difficult to understand a variety of physical, chemical and biological phenomenon directly-related to molecules, but it become meaningful to challenge in these researches. In my laboratory, multidisciplinary researches on mysterious and interesting molecular science and information technology are being performed. Specifically, our original molecular simulation tools based on the computational chemistry and chem.-bio-informatics has been developed and are contributing to solving many fundamental and/or industrial problems: medicinal drug-discovery assistance, elucidation of biological phenomenon, and also highly accurate predictions for physical and chemical properties of nano- and bio-materials.
Theme1:Development of high-performance and high-accuracy molecular simulation technology
Overview
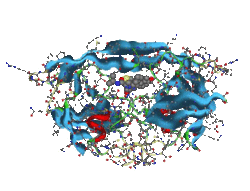
Molecular simulation is a powerful tool for supporting various researches on molecules existed in the immediate environment such as molecular design of medicinal and agrichemical drugs, and also new functional nano/bio-materials. For example, in a research of HIV-1 protease, many states where a ligand molecule (inhibitor) bounded at an active site can be calculated precisely, and an inhibited process of protease function can be understood by the aid of the graphical representations (Figure 1). In addition, modification and replacement of the inhibitor (high-throughput virtual screening), high-accurate energy evaluations by using thermal dynamics of the protease-ligand complex, those challenging will be able to contribute to seeking a new medicine which has more powerful and fewer side-effects. Moreover, practical applications to high-speed analysis for large-scale molecular simulation are realized by introducing parallel distributed processing technology to our computational tools.
Keywords
Theme2:Development of analytical technology of crystal polymorphism
Overview
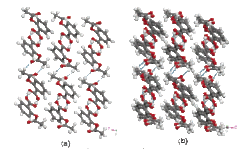
In the R & D from medicines to functional materials, one of the common important problems is a prediction method of crystal polymorphism. In other words, when a molecule can be crystallized with some different packing forms, a part of the grown crystals may show unexpected chemical/physical properties and medicinal effect. For example, aspirin is known as analgesic and antipyretic drug, and the second crystal structure “form II” that is slightly different from conventionally-known “form I” was recently discovered (Figure2). Our crystal simulation technology can be used to calculate the lattice energies of these crystalline structures, activated energies of the crystal phase transformation, and the sublimation and melting energies, and then, make it is possible to support bioavailability estimation such as the medicinal effects due to the crystal polymorphism.