
ここからコンテンツです。

Assembly of fluctuating molecules in artificial cell membranes
Domains of hydrophilic-polymer-modified lipids in lipid bilayer membranes By Ryugo Tero
Ryugo Tero at Toyohashi University of Technology has, in cooperation with Kanazawa University, discovered the aggregates of a hydrophilic-polymer-modified lipid in a lipid bilayer membrane. An unexpected phenomenon whereby the aggregated bulky polymer appeared lower in the atomic force microscope topography was discovered, and the related causes were revealed. These findings will lead to further understanding of the function of glycolipids and membrane proteins.
Lipids and membrane proteins existing in cell membranes, which form the outermost layer of cells, are responsible for recognizing extracellular environments and transferring that information inside the cell. Due to their deep relation to bacterial and viral infection, immunological response and neural transmission, they are important research topics in the fields of biology, medicine and drug development. In the reaction process of both external recognition and signal transfer, the formation of two-dimensional aggregates of lipids with bulky hydrophilic groups, such as sugar chains or inositol rings, are considered necessary in cell membranes. Small aggregates of up to 10 molecules are called clusters, while aggregates with more molecules and further growth are called domains.
Lipids are amphiphilic molecules derived from organisms, and have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties within their molecules. Many past studies have shown that interactions with the hydrophobic part, such as the phase transition and miscibility of hydrocarbon chains, play an important role in domain formation in lipid bilayer membranes. On the other hand, interactions with the hydrophilic part of lipids have not yet been widely researched, with many factors still remaining unclear. Interactions become complicated because of repulsion occurring through the fluctuation of hydrophilic properties in the water, particularly at bulky hydrophilic parts like sugar chains. The repulsion caused by such fluctuation also affects measurements via atomic force microscopy (AFM) that can detect even the tiniest amount of force.
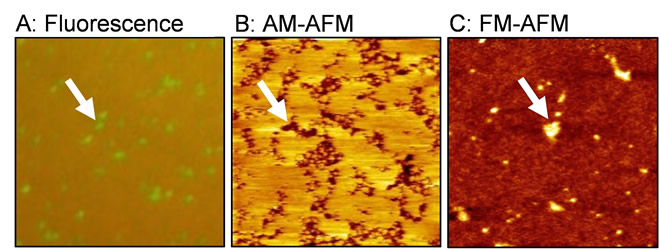
(A) Fluorescence image, (B) amplitude modulation (AM) AFM topography, and (C) frequency modulation (FM) AFM topography.
A research team helmed by Ryugo Tero, Associate Professor in Toyohashi University of Technology, has used fluorescence microscopy and AFM to examine in detail artificial lipid bilayer membranes containing lipids modified by the hydrophilic polymer, polyethylene glycol (PEG) (Figure 1). The results revealed that two types of aggregates, clusters and domains, form depending on the concentration of PEG-modified lipids, and that the there is almost no fluidity in the domains that appear due to high concentration. These aggregates are formed through the interaction not with lipids’ hydrophobic part, but rather with their hydrophilic part. Interestingly, when observed with AFM, the PEG-modified lipid domains that should have been bulky, were observed at a lower level than the surroundings (Figure 1B).
Associate Professor Tero implemented a joint experiment with Professor Takeshi Fukuma in Kanazawa University to determine the reasons for this. By utilizing frequency modulation AFM (FM-AFM), and accurately controlling the force between the sample and the probe, they were able to observe the PEG-modified lipid domain at a higher level than the lipid membrane area, without the application of any amount of force (Figure 1C). Since repulsions will change due to the fluctuation of hydrophilic polymer chains dependent on the force applied, it has been found that a reverse image of the true three-dimensional structure can always be observed during an amplitude modulation AFM (AM-AFM) observation (Figure 2).
"In order to establish an experimental method for examining glycolipids’aggregate state and function, we utilized PEG-modified lipids that are easy to obtain at the very beginning. We struggled to find the most suitable conditions for sample preparation and AFM observation of the lipid bilayer membrane containing PEG-modified lipids. The results differed greatly in comparison to expectations, especially due to the fact that the recessed areas grew relative to the increase in concentration of PEG-modified lipids. Thinking there might have been a mistake, we repeated the experiment and confirmed its reproducibility. Intuitively, it may seem unlikely that the region with bulky molecules appears lower with AFM, but when the assembled state of the polymer and the basic principles of AFM are considered, this is actually very reasonable.
“ The Eureka moment for our joint experimental group with Kanazawa University came when we observed how the concave-convex properties of the surface reversed after switching to FM-AFM” explains the main author, Yasuhiro Kakimoto. Mr. Kakimoto is currently enrolled in a doctoral course at Toyohashi University of Technlogy, as a part of the Program for Leading Graduate Schools organized by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology.
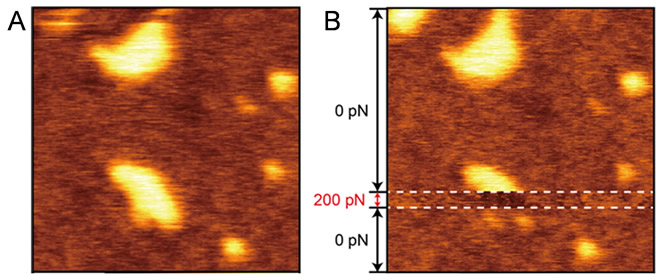
The research team leader, Associate Professor Ryugo Tero said ”In order to understand the functions of biomolecules at a molecular level, it is vital to comprehend the appearance of soft molecules, such as lipids and proteins, which fluctuate in water. In fact, some evidence from experimental areas containing many glycolipids being observed at a lower level with AM-AFM has been obtained over roughly the past 10 years in several systems. Although repulsion due to fluctuation of hydrophilic parts was only a hypothesis, this study has confirmed its validity. The crucial breakthroughs in this study were achieved thanks to Professor Fukuma’s state-of-the-art FM-AFM instrument (Figure 2), which made a key contribution to this joint research accomplishing magnificent results.”
The principle of domain formation due to interactions with hydrophilic polymer chains identified as a result of this research has been found to share commonalities with glycolipids in the cell membrane. Our research team is of the opinion that this principle will assist with the understanding of the mechanism of cell recognition and signal transfers related with the aggregate state of glycolipids and membrane proteins. Furthermore, the findings from the experiments, in which bulky objects can appear sunken-in depending on the conditions, will be valuable for the many researchers analyzing biological molecules underwater through atomic force microscopy. In addition, PEGs have the effect of suppressing nonspecific adsorptions such as proteins, etc., and can also be utilized in bio-interfaces and drug delivery. The formation and force response of PEG-rich clusters and domains are expected to have a pervasive effect also in these fields.
This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI Grant Numbers JP15H03768 and JP15H00893; CREST, Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) Grant Number JPMJCR14F3; A-STEP, JST. The first author Yasuhiro Kakimoto also received a grant as part of the Program for Leading Graduate Schools run by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Reference
Yasuhiro Kakimoto, Yoshihiro Tachihara, Yoshiaki Okamoto, Keisuke Miyazawa, Takeshi Fukuma, and Ryugo Tero (2018). Morphology and Physical Properties of Hydrophilic-Polymer-Modified Lipids in Supported Lipid Bilayers, Langmuir, 34(24), 7201-7209.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b00870
揺らぐ分子が細胞膜モデル内で作る集合体
親水性高分子修飾脂質が作る脂質二重膜内ドメインBy 手老 龍吾
豊橋技術科学大学の手老准教授らは金沢大学と共同で、親水性高分子鎖を持つ脂質分子が脂質二重膜に作る集合体とその物性を明らかにしました。また、かさ高い高分子鎖の集合体が原子間力顕微鏡で低く観察される反転現象を見出し、その原因を明らかにしました。これらの知見は、感染や免疫反応に関連する糖脂質や膜タンパク質の働きを理解し、そのための実験手法を開発することにつながります。
細胞外部の環境を認識してその情報を細胞内に伝える役目は、細胞の最外層に位置する細胞膜に存在する脂質と膜タンパク質が担っています。これらは細菌やウイルスの感染、免疫反応、神経伝達などに深く関わることから、生物学・医療・創薬分野での重要な研究対象です。外部認識や信号伝達の反応過程においては、糖鎖やイノシトール環などのかさ高い親水基を持つ脂質が細胞膜上で2次元的な集合体を形成することが必要であると考えられています。この集合体は10分子程度までの小さい物はクラスター、より多くの分子が集まり広く成長したものはドメインと呼ばれます。
脂質は生体に由来する両親媒性分子であり、分子内に親水的な部分と疎水的な部分を持ちます。脂質二重膜内でのドメイン形成において疎水性部位での相互作用、例えば炭化水素鎖の相転移や混和性(miscibility)、が主要な役割を果たすことが過去の多くの研究により示されてきました。一方、脂質の親水性部位の相互作用については研究が少なく、不明な点が多いです。特に糖鎖などのかさ高い親水性部位では、親水基が水中で揺らぐことで生じる斥力が生じるため、相互作用が複雑になります。この揺らぎによる斥力は、原子間力顕微鏡(AFM)のように微細な力を検出する計測手法にも影響を及ぼします。
豊橋技術科学大学の手老龍吾准教授のグループは、親水性高分子のポリエチレングリコール (PEG)で修飾した脂質を含む人工脂質二重膜を、蛍光顕微鏡およびAFMを用いて詳細に調べました。その結果、PEG修飾脂質の濃度に依存してクラスターとドメインの2種類の集合体が形成されること、高濃度で現れるドメインにはほとんど流動性が無いことを明らかにしました。これらの集合体は、脂質の疎水性部位ではなく親水性部位の相互作用で形成されていることを示しました。興味深いことに、AFM観察において、かさ高いはずのPEG修飾脂質ドメインは周囲よりも凹んで観察されました。この理由について、手老准教授は金沢大学の福間剛教授と共同実験を行いました。周波数変調型AFM (FM-AFM)を用い、試料と探針の間の力を精密に制御することで、ほとんど力を印加せずに観察すればPEG修飾脂質ドメインが周囲の脂質膜領域よりも高く観察されることを明らかにしました(図1)。印加される力に依存して親水性高分子鎖の揺らぎによる斥力が変化するため、一般的な振幅変調型AFM (AM-AFM)観察の条件では真の立体構造とは反転した像が現れることが示されました(図2)。
「糖脂質の集合状態と機能を調べるための実験手法を確立するために、まずは入手が容易なPEG修飾脂質を用いました。PEG修飾脂質を含む脂質二重膜は、試料調製やAFM観察の最適な条件を見つけるのに苦労しました。特にPEG修飾脂質の濃度を増やすほど凹んだ領域が増えるのは予想とは全く違っていました。何かの間違いではないかと思い、実験を繰り返して再現性を確かめました。直観的には、かさ高い分子が多い場所がAFMで低く見えるとは考えられませんが、高分子の状態やAFMの原理についてよく考えると、実は非常に理にかなっているのです。金沢大学での共同実験で、FM-AFMに切り換えて表面の凹凸が反転した時にはとても興奮して、”やっぱりそうだ!”と叫んでいました。」と筆頭著者である博士後期課程の柿本恭宏(文部科学省博士課程教育リーディングプログラム履修生)は説明します。
研究チームのリーダーである手老龍吾准教授は、「脂質やタンパク質のようにやわらかい分子が水中で揺らぐ姿を捉えるのは、生体分子の機能を分子レベルで理解するために重要なことです。実は、糖脂質を多く含む領域がAM-AFMで低く観察されるという実験結果は、約10年前からいくつかの系で得られていました。親水性部位の揺らぎによる斥力が原因だろうと推測していましたが、この研究で裏付けられました。決定的だったのはやはり、福間教授の最先端のFM-AFM装置を用いた結果(図2)であり、素晴らしい共同研究成果だと思っています。」と話しています。
本研究成果によって得られた親水性高分子鎖の相互作用によるドメイン形成の原理は、細胞膜中の糖脂質などにも共通するものであり、糖脂質や膜タンパク質の集合体形成が関わる細胞認識や信号伝達の仕組みを理解するのに役立つと研究グループは考えています。さらに、かさ高いはずの物が条件によって凹んで見えうる、という実験上の知見は、原子間力顕微鏡で水中の生体分子を観察している多くの研究者にとって有用です。また、PEGはタンパク質などの非特異的吸着を抑制する作用があり、バイオインターフェースやドラッグデリバリーにも用いられています。PEG-richなクラスターおよびドメインの形成と力応答はこれらの分野にも波及効果があると期待されます。
本研究は、日本学術振興会(JSPS)科研費JP15H03768、JP15H00893、科学技術振興機構(JST) CREST (JPMJCR14F3)、JST A-STEPからの支援を受けて行われました。また、筆頭著者の柿本は文部科学省・日本学術振興会の実施する博士課程教育リーディングプログラムの支援を受けました。
Researcher Profile

| Name | Ryugo Tero |
|---|---|
| Affiliation | Department of Environmental and Life Sciences |
| Title | Associate Professor |
| Fields of Research | Surface physical chemistry |
ここでコンテンツ終わりです。
