
ここからコンテンツです。

Can robots recognize faces even under backlighting?
An adaptive contrast adjustment for illumination-invariant face appearance By Jun Miura
Jun Miura and his colleagues have developed a novel technique to address the problem of vision-based face detection and recognition under normal and severe illumination conditions. This technique contributes to help robotic systems that use face information for providing user-dependent services to work well under a large variety of illumination conditions.
Vision-based face detection and recognition is one of the most rapidly growing research areas in computer vision and robotics and is widely used in several human related applications. However, vision-based face detection and recognition has been shown to be effective only under normal illumination conditions. In developing an algorithm for face detection and recognition, it is crucial to consider both normal and severe illumination conditions. One approach is to convert face images under various illumination conditions into ones with invariant face appearance while preserving the face-specific characteristics such as texture and facial features.
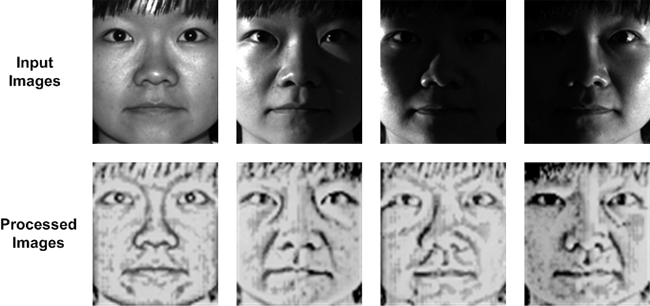
Now, researchers at the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at Toyohashi University of Technology have developed a novel technique to adaptively adjust the effect of lighting on human faces by employing an extended reflectance model. The model has one variable (illumination ratio), which is controlled by Fuzzy Inference System (FIS). To cope with a vast variety of illumination conditions, the FIS rule was optimized using Genetic Algorithm (GA).
The first author PhD candidate, Bima Sena Bayu Dewantara, explained, “To eliminate the effects of light, image contrast should be adjusted adaptively. To produce an invariant face appearance under backlighting, for example, cheeks need to be brightened, while the eyeballs must be kept dark. Such an adaptive contrast adjustment can be performed using the developed reflectance model, and we have shown that a combination of Fuzzy Inference System (FIS) and Genetic Algorithm (GA) is very effective for implementing the model."
Professor Jun Miura said, "By just adding this contrast adjustment to present face recognition systems, we can significantly improve the accuracy and performance of face detection and recognition. Moreover, this adjustment runs in real-time, and therefore, it is appropriate for real-time applications such as robot and human-interaction systems.”
A face not only provides a person's identity but also provides other information such as a person’s focus of attention and the degree of tiredness. Obtaining such information is useful for smooth human–machine interaction, and researchers expect that the proposed contrast adjustment method will also be useful in various situations, especially under severe illumination conditions.
This study was partly supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research No. 25280093 by JSPS, Japan.
Reference
Bima Sena Bayu Dewantara and Jun Miura (2016). OptiFuzz: A robust illumination invariant face recognition and its implementation, Machine Vision and Applications, DOI: 10.1007/s00138-016-0790-6.
ロボットは逆光でも人の顔を見分けられるか?
顔の見え方を照明条件によらず一定にするための適応的なコントラストの調整情報・知能工学系 三浦純教授らの研究グループがさまざまな照明条件下で顔の発見と認識が可能になる新たな手法を開発しました。この手法により、顔の特徴を使って利用者を認識し、利用者に応じたサービスを提供するロボットが、厳しい照明条件下でも動作できるようになります。
画像による顔の発見と認識は、顔認証によるセキュリティシステムや人をサポートするロボットなどの応用に幅広く利用されています。これまでの多くの手法は通常の照明下でのみ有効でしたが、実際の応用を考えると通常の照明下だけでなく厳しい照明の下でも動作することがとても重要です。そのための一つのアプローチは、さまざまな照明下での顔の画像を、顔特有の模様や特徴を維持しつつ一定の見え方になるように変換することです。例えば、逆光下では顔全体が暗くなりますが、画像変換により、頬は明るくする必要がありますが、瞳は暗いままにしておかなければなりません。
そこで、本学の情報・知能工学系の研究グループ(博士後期課程学生 Bima Sena Bayu Dewanntaraおよび三浦教授)は、拡張された光の反射モデルを用いて照明の影響を適応的に調整する新たな手法を開発しました。このモデルは調整可能な一つの変数(illumination ratioと呼ぶ)を持ち、その変数をファジィ推論システムによって制御します。そして、さまざまな照明条件に対応するため、推論システムが利用するファジィ推論規則を遺伝的アルゴリズム(GA)によって最適化しておきます。
提案する画像変換処理を現存の顔認識システムに追加するだけで、顔の発見と認識の性能を大幅に向上させることができます。さらに、この変換は実時間で行えるので、ロボットや人とやり取りをするシステムのような実時間動作が必要な応用に適しています。
顔は人の識別に役立つだけでなく、注意を向けている方向や疲れの程度など人のさまざまな情報を提供します。そのような情報を得ることは、人間と機械の間の快適なやり取りに有効であり、今回開発した顔画像変換手法はさまざまな応用において、特に厳しい照明条件下で有効に利用されることを期待しています。
本研究成果は、平成28年7月15日(金)にMachine Vision and Applications誌上に掲載されました。
本研究の一部は科研費25280093の支援を受けて実施されました。
Researcher Profile

| Name | Jun Miura |
|---|---|
| Affiliation | Department of Computer Science and Engineering |
| Title | Professor |
| Fields of Research | Intelligent Robotics / Robot Vision / Artificial Intelligence |
ここでコンテンツ終わりです。
