Akiduki, Takuma
| Affiliation | Department of Mechanical Engineering |
|---|---|
| Concurrent post | Research Center for Future Vehicle City |
| Title | Assistant Professor |
| Fields of Research | Digital Signal Processing, Soft Computing |
| Degree | Doctor of Engineering |
| Academic Societies | The Society of Instrument and Control Engineers, The Japanese Society of Artificial Intelligence, The Robotics Society of Japan, The IEEE Systems, Man, and Cybernetics Society, |
| akiduki@me Please append ".tut.ac.jp" to the end of the address above. |
|
| Laboratory website URL | http://is.me.tut.ac.jp |
| Researcher information URL(researchmap) | Researcher information |
Research
In my work, the paradigm of the nonlinear dynamical systems is used for extracting and classifying from human-related data. Examples of the human-related data include that human motion, behavior, and medical/health data, which contain the both components of strong noise and wide fluctuation from individual characteristics of the person.
Theme1:Cellular Neural Networks and Its Applications
Overview
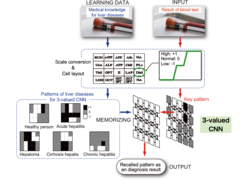
Cellular neural networks (CNNs) are one type of interconnected neural network and differ from the well-known Hopfield model in that each cell has a piecewise linear output function. In my study, a multi-valued CNN model in which each nonlinear element consists of a multi-valued output function has been proposed. In addition, the proposed multi-valued CNN has been applied to a diagnosis disease problem. The results obtained show that the multi-valued CNN improves classification accuracy by appropriately selecting the output level q. Moreover, these results also show that the multi-valued associative memory can expand both the flexibility of designing the memory pattern and its applicability.
Selected publications and works
1) T.Akiduki, et al., Design of Multi-Valued Cellular Neural Networks for Associative Memories, Int. J. of Innovative Computing, Information and Control, Vol.8, No.3, pp.1575--1589 2012.
2) T.Akiduki, et al., Associative Memories with Multi-Valued Cellular Neural Networks and Its Application to Disease Diagnosis, Proc. of the IEEE SMC 2009, pp.3924--3929, 2009.
Keywords
Theme2:Human Motion Analysis using Attractors
Overview
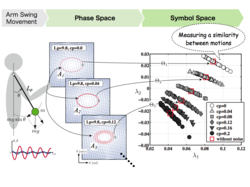
In this study, we focus on a time-series analysis method for human motion analysis based on symbolization of sensor data. Human movements are observed by motion sensors such as accelerometers and gyroscopes, which involve time series. Time series of movements can often be represented as periodical signals. In our approach, the time series of the periodic signals are expressed by dynamical systems having attractors, which symbolize the time series in state space. Moreover, the symbol space is designed from a set of attractors to classify/partition symbols. In the past, we have discussed similarity measures for motion in the symbol space by using simulation. The aim of this simulation was to investigate the relationship between the physical conditions of motion and the distribution of symbols in the symbol space. The results suggested that symbol space can be used to discriminate motions.
Selected publications and works
1) T. Akiduki, et al. , ``Feature Extraction of Motion from Time-series Data by using Attractors'', IEEJ Transactions on Electronics, Information and Systems, Vol.132, No.6, pp.975--982, 2012.
2) T.Akiduki, et al., Human Motion Analysis from Inertial Sensor Data Based on Nonlinear Dynamics, Proc. of the IFAC WC 2011, pp.7396--5194, 2011.