Yokoyama, Hiroshi
| Affiliation | Department of Mechanical Engineering |
|---|---|
| Title | Professor |
| Fields of Research | Fluid engineering, Aeroacoustics, Computational fluid dynamics, Thermoacoustics |
| Degree | Doctor of Philosophy in Engineering (The University of Tokyo) |
| Academic Societies | Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan, The Visualization Society of Japan, The Japan Society of Fluid Mechanics, The American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics |
| h-yokoyama@me Please append ".tut.ac.jp" to the end of the address above. |
|
| Laboratory website URL | https://ec.me.tut.ac.jp/ |
| Researcher information URL(researchmap) | Researcher information |
Research
Abstract
I am interested in complex phenomena related with fluid-dynamics, aeroacoustics, thermodynamics, and EletroHydroDynamics. Especially, my objective is to establish design guide for high efficiency and reduced noise for automobiles, high-speed train and fluid-related machinery. Acoustic radiation around musical instruments is also my topic. Simulations using high-performance computers and wind tunnel experiments are performed. I completed my Ph.D (2010) for research of cavity tone after undergraduate studies at The University of Tokyo. I studied as a visiting academic in University of Southampton in U.K (2015-2016). I have been working in the department of mechanical engineering at Toyohashi University of Technology and a cooperative research fellow at The University of Tokyo since 2010.
Main themes
- Research for conservation of energy in fluid machinery or thermoacoustic device utilizing acoustic power and wasted heat
- Control of Aerodynamic noise generated from high-speed transports and fluid equipments
- Coupled problems such as acoustic radiation from musical instruments
Key words
Energy conservation, Aeroacoustics, Noise, Fluid machinery, Turbulence, Computational fluid dynamics, Cavity, Fan, Plasma actuators, Musical instruments, High-speed vehicles
Main publications
- H. Yokoyama, I. Tanimoto, A. Iida,"Experimental Tests and Aeroacoustic Simulations of the Control of Cavity Tone by Plasma Actuators", Appl. Sci. 2017, 7(8), 790, pp.1-15; doi:10.3390/app7080790.(The figures of this paper was on cover page of this issue)
- T. Miyamoto, H. Yokoyama, A. Iida,"Suppression of Aerodynamic Tonal Noise from an Automobile Bonnet Using a Plasma Actuator", SAE Int. J. Passeng. Cars - Mech. Syst. 10(3):2017, pp.22-30. doi:10.4271/2017-01-1825.
- H. Yokoyama, Y. Hirose, A. Iida, "Effective mixing and aeration in a bioreactor with Taylor vortex flow", Mechanical Engineering Letters, 2, 16-00412, pp.1-9, 2016
- H.Yokoyama H, A. Miki, H. Onitsuka, A. Iida, "Direct numerical simulation of fluid-acoustic interactions in a recorder with tone holes", Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 138(2), pp.858-873,2015
- H. Yokoyama, K. Kitamiya, A. Iida, "Flows around a cascade of flat plates with acoustic resonance", Physics of Fluids, 25(10), 106104-1-106104-22, 2013
- H. Yokoyama, C. Kato, "Fluid-acoustic interactions in self-sustained oscillations in turbulent cavity flows. I. Fluid-dynamic oscillations", Physics of Fluids, 21(10), 105103-1-105103-13, 2009
- H. Yokoyama, Y. Tsukamoto, C. Kato, A. Iida, "Self-sustained oscillations with acoustic feedback in flows over a backward-facing step with a small upstream step", Physics of Fluids, 19(10), 106104-1-106104-8, 2007
Academic networks: researchmap Google scholar ResearchGate ORCiD Scopus
Theme1:Clarification of radiation mechanism and control for aerodynamic sound
Overview
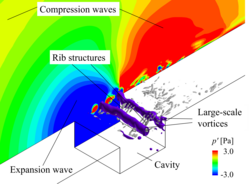
Aerodynamic noise increases in proportional to the high power of velocity. So, the noise is a sever problem for high-speed transport vehicles or flow-related machinery. For example, intense tonal sound radiates from cavity flow and flow around a cascade of flat plates, where the feedback loop due to fluid-acoustic interactions occurs. To clarify the mechanism of acoustic radiation and establish the methodologies for noise reduction, we perform wind tunnel experiments and aeroacoustic direct numerical simulation (AADNS).
Selected publications and works
- H. Yokoyama, K. Minowa, K. Orito, M. Nishikawara, H. Yanada, Compressible Simulation of Flow and Sound around a Small Axial-Flow Fan with Flow through Casing Slits, Journal of Fluids Engineering, Transactions of the ASME, 142(10), 101215, pp.1-10, 2020
- H. Yokoyama, A. Miki, H. Onitsuka, A. Iida, "Direct numerical simulation of fluid-acoustic interactions in a recorder with tone holes", Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 138(2) 858-873, 2015
- H. Yokoyama, K. Kitamiya, and A. Iida, Flows around a cascade of flat plates with acoustics resonance, Physics of Fluids, 25(10), 106104, 2013.
- H. Yokoyama and C. Kato, Fluid-acoustic interactions in self-sustained oscillations in turbulent cavity flows. I. Fluid-dynamic oscillations, Physics of Fluids 21, 105103, 2009.
Keywords
Theme2:Flow control with application of electrohydrodynamic and thermoacoustic phenomena
Overview
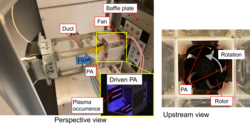
To realize innovative fluid machinery, electric control of flow and acoustic fields with methodologies such as plasma actuators is studied. Studies for clarification of coupled phenomena between the thermoacoustic and aeroacoustic phenomena are conducted, where thermoacoustic phenomena mean conversion between thermal and acoustic energies.
Selected publications and works
- Hiroshi Yokoyama, Nobuaki Nagao, Kazuma Tokai, Masahito Nishikawara, Control of Flow and Acoustic Fields Around an Axial Fan Utilizing Plasma Actuators, Transactions of the ASME, Journal of Fluids Engineering, 147(1), 011201, 2024. DOI:10.1115/1.4066112
- H. Yokoyama, Y. Omori, M. Kume, M. Nishikawara, H. Yanada, Simulation of thermoacoustic heat pump effects driven by acoustic radiation in a cavity flow, International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 185, 122424, pp.1-17, 2022
- H. Yokoyama, K. Otsuka, K. Otake, M. Nishikawara, H. Yanada, Control of Cavity Flow with Acoustic Radiation by an Intermittently Driven Plasma Actuator, Physics of Fluids, 32(10),106104, pp.1-20, 2020
Keywords
Theme3:Research for CO2 physisorption
Overview
Research for carbon dioxide physisorption is conducted for establishing of separation technology of greenhouse gas in exhausted gas from various plants.
Selected publications and works
- H. YOKOYAMA, K. Mochizuki, M. Nishikawara, Promotion of carbon dioxide adsorption using a zeolite-coated monolith with acoustic excitation, Bulletin of the JSME, Journal of Fluid Science and Technology, 19 (3), 24-00119, 2024
- H. Yokoyama, Y. Hirose, A. Iida,Effective mixing and aeration in a bioreactor with Taylor vortex flow, Mechanical Engineering Letters, 2(16-00412) 1-9, 2016
Keywords
Title of class
○Fluid Mechanics (B11620110)
○Fluid Energy Conversion (B11624090)
○Computational Fluid Dynamics (M21624170)
〇Advanced Fluid and Energy Engineering (M41630540)
○Advanced Environmental Engineering (D51030080)
Others (Awards, Committees, Board members)
Awards
- Mar. 2023, The NAGAI Foundation for Science & Technology, Academic Award
- Apr. 2019, The Commendation for Science and Technology by the Minister of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, The Young Scientists
- May 2018, The Asahara Science Award, Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan
- Apr. 2012, JSME Medal for Outstanding Paper, The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- Apr. 2011, JSME Young Engineers Award, The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers
- Mar. 2007, Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan, Prediction of tonal sound from side mirror, Best paper award
Committees, Board members (this year)
- Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan, Director
- The Japan Society of Fluid Mechanics, Delegate
- The Visualization Society of Japan, Delegate
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, Tokai Branch, Secretary