

Creation of training data to estimate the physical state of care robot users
Creating training data from a human body link model without measurements Mizuki Takeda
A research team led by Assistant Professor Mizuki Takeda from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Toyohashi University of Technology, has developed a technique to generate training data for robots that operate based on estimations of the user’s state using machine learning. Previously, research a method had been proposed to estimate the condition of robot users based on machine learning which used candidate points for the position of the center of gravity. However, for such learning, training data corresponding to when the robot is used to support movements are required. The above-mentioned research team developed a method of creating training data by using a human body link model without the need to analyze the movements.
The development of robots supporting frequently performed tasks such as standing up and walking is progressing as elderly people with weakened muscles often require assistance in their daily lives. In order to reduce the burden on caregivers, robots must be able to automatically perform supportive actions. To achieve this, it is necessary to estimate the condition of the elderly person using the robot and provide assistance appropriate to that condition. Currently, the research team has proposed a method for calculating the candidate positions of the center of gravity of the robot user and estimating their physical state using machine learning. However, this method requires the acquisition of the user's movements during use of the robot as teacher data, and in particular, the measurement of data for abnormal conditions (such as when the user is about to fall over while walking) could be burdensome for the elderly.
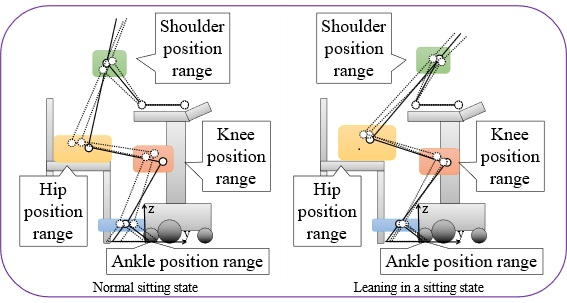
The human posture in states such as sitting (left) and leaning forward in a sitting state (right) is represented by a link model, and candidate positions for center of gravity are calculated to create training data.
To solve this problem, the research team developed a method to generate candidate center-of-gravity teacher data without measuring movements by using a human body link model. The human body link model is a simple model representing the human body with rigid links and rotating joints. This model can be used to simulate human positions in various states such as sitting and standing, as well as abnormal states, and in this way generate training data. Experiments have confirmed that the care robots can learn based on the training data created by this method, estimate the user’s state, and support standing up, walking, and sitting down actions.
The research team believes that the developed training data creation method based on the human body link model can be applied to care robots of various shapes and serving various purposes. Moreover, it can be applied to industrial and communication robots that rely on estimating the condition of humans and operating accordingly. In the future, we aim to realize a more secure and user-friendly system in which the robot not only operates based on the estimation, but also provides necessary information to the user so that the human and robot can communicate well with each other.
Reference
Mizuki Takeda and Kaiji Sato (2023). Training Data Generation Using Human Link Model for State Estimation of Care Robot User. IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp.69310-69325.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3292344
福祉ロボット使用者の状態推定のための教師データ作成
計測せずに人体リンクモデルから教師データを作成する 武田 洸晶豊橋技術科学大学機械工学系の研究チーム(武田洸晶助教ら)は、機械学習により、使用者の状態を推定して動作するロボットのための教師データの作成手法を開発しました。これまでに、重心位置の候補点を用いて機械学習によりロボット使用者の状態を推定する手法を提案してきましたが、その学習には、ロボットを用いて動作を行った際のデータが教師データとして必要でした。今回の研究では、人体リンクモデルを利用することで、動作の計測を行わずに教師データを作成する手法を実現しました。
筋力の衰えた高齢者に向けた日常生活の支援が望まれており、特に頻繁に行う起立や歩行などを支援するロボットの開発が進んでいます。介護士の負担を減らすためにも、ロボットは自動で支援動作を行うことが求められ、そのためには、ロボットを使用する高齢者の状態を推定して、その状態に適した支援を行う必要があります。研究チームはこれまでに、ロボット使用者の重心位置の候補を計算し、機械学習により状態を推定する手法を提案してきました。しかし、この手法では、ロボットを使用している際の使用者の動作を教師データとして取得する必要があり、特に異常状態(歩行中に使用者が転倒しそうな状態など)のデータの計測は高齢者の負担になる可能性がありました。
そこで研究チームは、人体リンクモデルを用いることで、動作を計測せずに重心候補の教師データを作成する手法を開発しました。人体リンクモデルは、剛体リンクと回転関節により人体を簡易的に表したモデルです。そのモデルを利用して座位や立位、異常状態などの各状態における人間の姿勢をシミュレートし、教師データを作成することができます。この手法で作成した教師データを学習し、実際に福祉ロボットで使用者の状態を推定して起立・歩行・着座を支援できることを実験で確認しました。
研究チームは、人体リンクモデルを用いた教師データ作成手法は様々な形状・用途の福祉ロボットに適用可能であると考えています。また、福祉ロボットだけでなく、人間の状態を推定して動作する必要がある産業用ロボットや、コミュニケーション・ロボットへの応用も期待されます。今後は、推定に基づいてロボットが動作するというだけでなく、ロボットから使用者に必要な情報を提示して、人間とロボットがうまくコミュニケーションを取ることで、より安心できて使いやすいシステムを実現することを目指しています。
Researcher Profile

| Name | Mizuki Takeda |
|---|---|
| Affiliation | Department of Mechanical Engineering |
| Title | Assistant Professor |
| Fields of Research | Robotics / Human-Robot Interaction / Care Robot / Robot Ethics |
