ここからコンテンツです。

Phytoplankton dicrateria rotunda synthesizes hydrocarbons equivalent to petroleum
Yuu Hirose
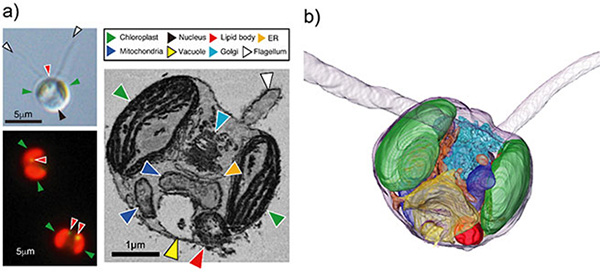
Director-General Naomi Harada and colleagues from the Research Institute for Global Change at the Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology, in collaboration with Assistant Professor Yuu Hirose from Toyohashi University of Technology and Specially Appointed Professor Kazuyoshi Murata from the National Institute for Physiological Sciences, discovered that the phytoplankton Dicrateria rotunda (D. rotunda) can synthesize a series of saturated hydrocarbons with a carbon number ranging from 10 to 38*. The saturated hydrocarbon content of the D. rotunda ARC1 increased under dark and nitrogen-deficient conditions. Understanding the physiological function and synthesis pathways of these saturated hydrocarbons may contribute to the development of biofuels in the future.
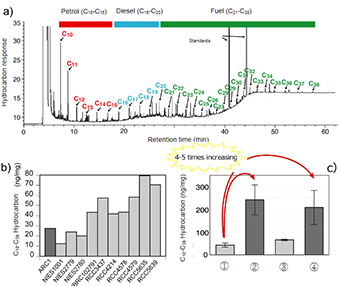
A phytoplankton community was collected from seawater of the Chukchi Sea during a science cruise of the research vessel "Mirai" in the Arctic Ocean in 2013, from which we isolated and cultured the Arctic strain of D. rotunda, ARC1. ARC1 contained a series of saturated hydrocarbons with carbon numbers ranging from 10 to 38, which puts them in the range of petrol (carbon number 10 to 15), diesel oils (carbon number 16 to 20), and fuel oils (carbon number 21 or higher). Moreover, we examined ten additional strains of Dicrateria stored in culture collections, all of which were found to be similarly capable of hydrocarbon synthesis, indicating that this was common to the entire Dicrateria genus. This study is the first to report on an organism with the capability to synthesize hydrocarbons equivalent to petroleum.
The capability of the ARC1 strain to synthesize saturated hydrocarbons was shown to increase depending on the environmental conditions, and the findings of this study are expected to contribute to the development of biofuels in the future.
This study was supported by JSPS Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research JP22221003 and JP15H05712.
* Saturated hydrocarbons: Organic compounds composed of carbon and hydrogen. The saturated hydrocarbon with the smallest mass number is methane (CH4), which has a carbon number of one.
Reference
Naomi Harada, Yuu Hirose, Song Chihong, Hirofumi Kurita, Miyako Sato, Jonaotaro Onodera, Kazuyoshi Murata, Fumihiro Itoh (2021) "A novel characteristic of a phytoplankton as a potential source of straight-chain alkanes" Sci. Rep. 11, 14190, 10.1038/s41598-021-93204-w.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-93204-w
植物プランクトンDicrateria rotundaが石油と同等の炭化水素を合成する能力をもつことを発見
広瀬 侑
環境生命・応用工学系の広瀬侑助教は、国立研究開発法人海洋研究開発機構(以下「JAMSTEC」という。)地球環境部門の原田尚美部門長、生理学研究所の村田和義特任教授らとともに、植物プランクトンDicrateria rotunda (D. rotunda)が炭素数10から38まで一連の飽和炭化水素*を合成する能力をもつことを発見しました。また、微生物株保存機関に保管されている他10種のDicrateria属を調べたところ、すべての株が同様の合成能力をもち、本種に共通した能力であることが明らかとなりました。このような石油と同等の炭化水素を合成する能力を持つ生物は、世界で初めての発見です。本種の飽和炭化水素の合成能力は環境条件により増加する結果(図 3c)も得られており、今後のバイオ燃料開発につながる可能性が期待されます。
本研究グループは、海洋地球研究船「みらい」による2013年の北極海の研究航海において、北極海の海氷減少に伴い、ベーリング海に生息する植物プランクトンが北極海へ侵入し、現場で生産をしているかどうか調査する目的で植物プランクトンを採取していました。そのうち単離培養が可能な植物プランクトンについて、いくつかの種類の単離培養を実施し、ハプト藻に特有の有機化合物を持つか否かを確認していたところ、Dicrateria rotunda (D. rotunda)北極海株ARC1が炭素数10から38までの一連の飽和炭化水素合成することを発見しました。この組成は、ガソリン(炭素数10から15)、ディーゼル油(炭素数16から20)、燃料油(炭素数21以上)と同等でした。このような炭化水素合成能力を持つ生物は過去に報告例がなく、本研究の成果は初めての発見となるものです。Dicrateria自体は太平洋や大西洋など他の海域でも広く生息することがわかっています。そこで、日本、フランスの植物プランクトンのカルチャーコレクションに保有されている10種のDicrateria属の炭化水素組成を調べたところ、すべての株で、北極海株ARC1と同じく炭素数10から38までの一連の飽和炭化水素を合成する能力を持つことを確認しました。つまり、石油と同等の炭化水素をつくる能力はDicrateria属に共通の能力であることがわかりました。今回調査した11株では、飽和炭化水素の中でも特に炭素数10および11の短い炭素数の飽和炭化水素をより多く合成する特徴を持っていることも明らかにしました。
続いて本研究グループは、北極海株ARC1を用いて、光・温度・窒素栄養塩濃度などの条件を変えた際の、炭化水素量の変動を調査しました。その結果、光合成が止まった暗条件や窒素栄養塩を欠乏させた条件で、細胞サイズが縮小するとともに、飽和炭化水素の総量が約5倍程度に増加することがわかりました。通常、飽和炭化水素がエネルギー貯蔵物質として使われている場合、光合成ができない暗条件ではエネルギー源として消費され、細胞内の含有量が低下するはずです。ところが、一連の飽和炭化水素量は暗所で増加したことから、エネルギー貯蔵物質としては機能していないと考えられました。最近の研究では、シアノバクテリアという別の光合成細菌において、炭素数15から19の飽和炭化水素は、主に葉緑体のチラコイド膜や細胞膜に蓄積して柔軟性を高めることが示唆されています。従って、北極海株ARC1においても、光や栄養塩が得られないストレス条件において、飽和炭化水素を細胞膜に蓄積することで、細胞や葉緑体の縮小を助けているのかもしれません。今後、一連の飽和炭化水素の生理的な役割の解明が期待されます。
D. rotundaのつくる一連の飽和炭化水素の成分は石油と同等であり、「質」としてはバイオ燃料として申し分ありません。一方で、合成する「量」には課題があります。例えば、D. rotundaの単位細胞量あたりの炭化水素含有量は、生物源オイルとしてこれまで利用されてきた実績のあるBotryococcus brauniiの2.5-20%程度しかありません。今後は、いかにD. rotundaの飽和炭化水素合成能を効率的に増強させるかが課題となります。そのためには、飽和炭化水素の合成条件の最適化や、育種や遺伝子改変による合成量の増加、飽和炭化水素合成遺伝子群の特定と異種の生物を用いた飽和炭化水素生産系の構築など、多くの基礎的研究が必要です。進行する地球温暖化を抑制するためには、人類のエネルギー消費の約85%を占める化石燃料の一部をバイオ燃料に置き換える必要があります。そのためには様々なアプローチによるバイオ燃料開発を進める必要があり、今回の発見は、我々の今後に有望な選択肢を与えるものです。北極海は、人類の研究の手が未だに及んでいない未踏の地であり、JAMSTECの航海や、文部科学省の北極域研究加速プロジェクト(ArCSⅡ)が進められています。これらのプロジェクトによって、人類の持続的な発展に貢献できる新たな有用生物が見つかる可能性があります。
*飽和炭化水素:炭素と水素からできている有機化合物。もっとも質量数の小さいものは炭素数が1つのメタン(CH4)。
Researcher Profile

| Name | Yuu Hirose |
|---|---|
| Affiliation | Department of Applied chemistry and Life Science |
| Title | Assistant Professor |
| Fields of Research | Photobiology, Genome Biology |
ここでコンテンツ終わりです。