Tech-Overtures
Spoken Term Detection: On-line tool for rapidly detecting spoken words in speech and video
A massive amount of speech and video content is stored on servers run by video-sharing sites, broadcast stations, call centers, e-learning host services, and other such organizations.
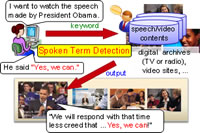
Spoken Term Detection (STD), which the enables search for a keyword on the speech/video database (Fig.1), is one of the essential technologies for effectively utilizing such information.
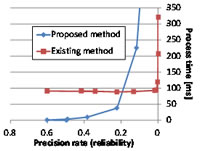
Kouichi Katsurada and Tsuneo Nitta at the Toyohashi University of Technology (Toyohashi Tech) have developed a rapid STD method that outputs the most reliable search results in a few milliseconds. The search speed is at least 10 times faster than existing methods (Fig.2).
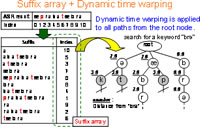
They researchers use a suffix array as a data structure and apply dynamic time warping on it to realize a high-speed ambiguous search (Fig.3). In addition, they embed keyword division and iterative lengthening search into the search algorithm. These techniques make it possible to detect a keyword on the speech/video database in a very short time.
This technique can be applied to search for a scene from movies, TV/radio programs, lecture videos, as well as being utilized at call centers for finding customer services information from the database.
The Toyohashi team is looking for partners to commercialize this powerful technology.
Further information
・ K. Katsurada, S. Teshima, and T. Nitta, Fast Keyword Detection Using Suffix Array, InterSpeech2009, 2147–2150, (2009).
・ Nitta-Katsurada website (Japanese only) : http://www.vox.cs.tut.ac.jp/~katurada/index-e.html
・ Office of Industry-Academia research (Japanese only): http://www.chizai.tut.ac.jp/
・ International affairs section
Toyohashi University of Technology
1-1 Hibarigaoka, Tempaku
Toyohashi, Aichi Prefecture, 441-8580, JAPAN
E-mail: ryugaku@office.tut.ac.jp
TEL: +81-532-44-6577
Enlarge Image
Fig.1 Spoken term detection
Enlarge Image
Fig.2 Search speed
Enlarge Image
Fig.3 Suffix array and dynamic time warping